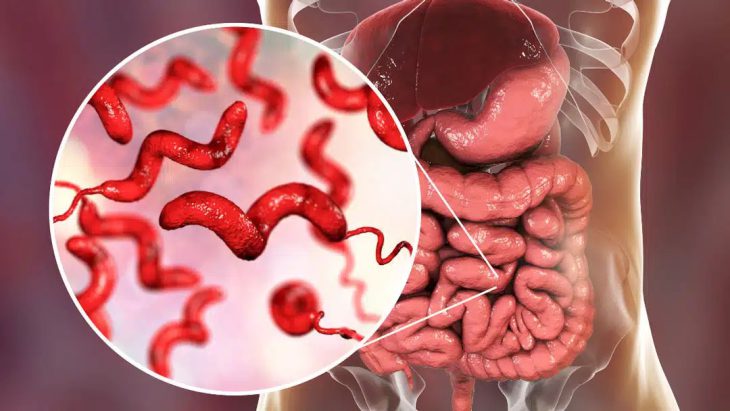
Campylobacter is one of the most common in the world. This disease causes the Diarrhea of and related diseases. According to the investigations, in most cases of campylobacter infection, this bacterium enters the body through medicinal foods. For this reason, you should avoid eating uncooked meat or undercooked meat. Milad Daro Company with a portable Real-Time PCR bag is ready to serve in the food and livestock sectors.
What are the symptoms of campylobacter infection?
what are the symptoms of campylobacter? Campylobacter disease symptoms usually appear two to five days after a person is infected with this disease. Therefore, symptoms may appear in a person as soon as he has this disease. The symptoms of these diseases usually change for the better. A person’s symptoms on the fourth day will be different from his symptoms on the ninth day. But in order to have an overview of this disease, some of the most common consequences of campylobacter are shared with you:
.Dysentery
.Abdominal pains
.stomach ache
.nauseous
.Headache
.Fever
The remarkable thing about Campylobacter infection is that many people do not experience all the complications caused by this disease at once. Therefore, even if one of the symptoms is also present in a person suspected of Campylobacter, additional investigations will be needed.
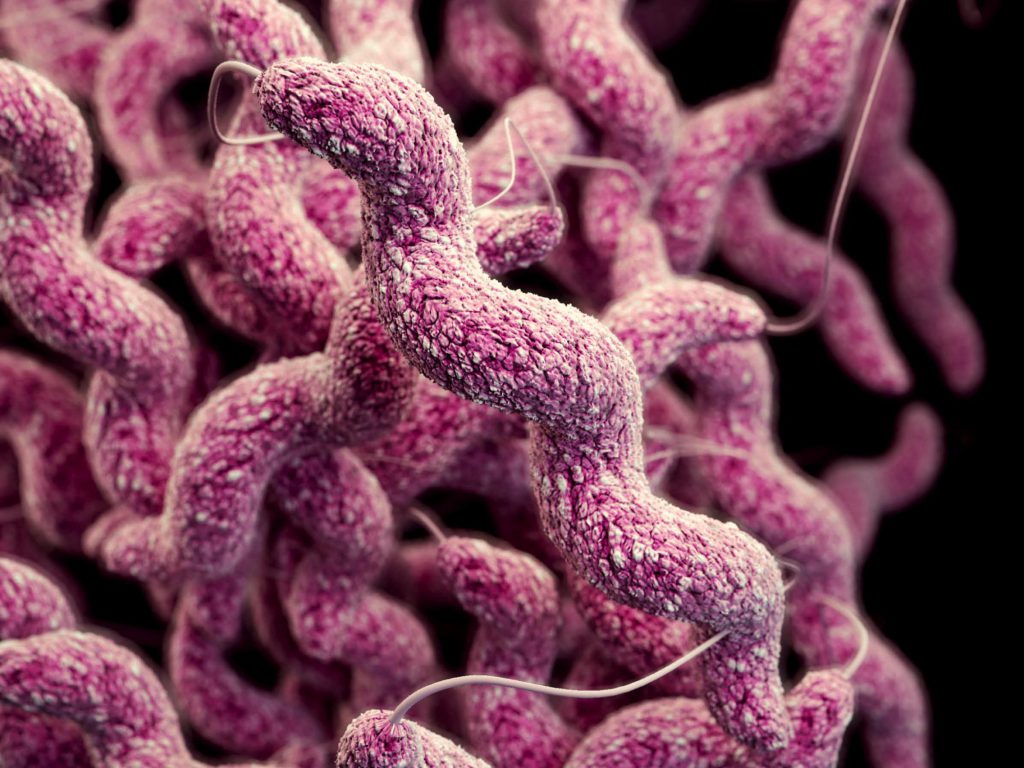
In 2023, a paper was published in Japan on Campylobacter. Campylobacter is food poisoning caused by the consumption of contaminated foods، especially poultry. Continuous quantitative measurement of Campylobacter spp. in contaminated foods is crucial to develop preventive measures. We developed a direct-qPCR method for determining the viable cell counts of Campylobacter spp. using qPCR without DNA extraction from enriched food samples and a sampling method (the wrap procedure) in which the sample is wrapped in a sheet, different from the conventional homogenization procedure.
Colonies were observed using the culture method, but their quantification was difficult due to swarming or their low number. However, estimating viable cell counts using the combination of wrap procedure and direct-qPCR methods is possible. The developed method can provide baseline data for the risk assessment Campylobacter food poisoning.
Source: PubMed
Write Your Comment