What happens is that the glucose or blood sugar is very high, by the time you can leave the body, it does not produce any insulin, or the insulin is not produced correctly and in the required amount in the body.
There are different types of selection: type 1 and selection, type 2 and selection , Gestational diabetes
People with people with special type. They must take any insulin to survive. Patients may forget to inject insulin. Considering this important issue, Stanford has succeeded in developing a drug delivery system based on hydrogel, which eliminates the need for annual drug injections and releases drugs into the body.
An injection every four months
A team from Stanford University has developed a new hydrogel that contains four months of drug for a drug treatment. that other patients do not need to take daily drugs, and the hydrogel releases drugs in the right dose for a long time. The hydrogel is liquid and easily injected with regular needles, and is solid and stable enough to last in the body for four months. This hydrogel material can make it easier for people to take drugs, improve patients’ quality of life, and reduce management-related complications.
Experiments in animal models
The study of the studies was done on the mouse model and they concluded that the emerging drug can control the GLP of the drugs and control the weight of the drugs.
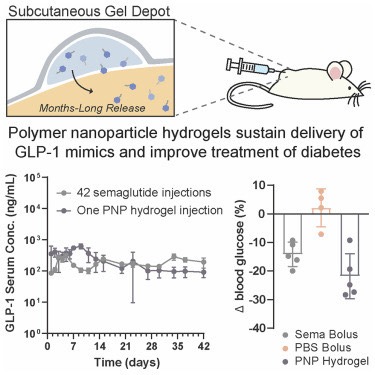
As a result, these injections are performed on mice with a certain type of disease, and the injection of hydrogel containing the drug every 42 days leads to better blood sugar management than the daily use of conventional drugs. According to the research team, this 42-day routine in mice is equivalent to four months in humans. The hydrogel creates a network structure that holds the drug in place and slowly dissolves in the body when it’s time to deliver the drug.
These results indicate that semaglutide can be more concentrated in the first week of release from the hydrogels, followed by long-term release. It creates anti-antibodies to the peptide with GLP-1 RA.
About 500 million people in the world have or already have the disease, making it one of the most expensive diseases in the world.
Within 1.5 to 2 years after testing and successfully discovering his new technology on pigs, the researcher will start human studies. The statistical results of the work done have been published in the journal Cell.
Write Your Comment