fowl adenovirus(FAdV) was first reported in Angara Goth, Pakistan in 1987. Also in June 2015, an outbreak of fowl adenovirus occurred in China, causing significant economic damage to the poultry industry.FAdV infections associated with IBH, HHS and GE are reported worldwide and cause significant economic damage in the poultry industry. Various types of vaccines have already been developed and evaluated to control HHS, and several inactive combination vaccines have been developed that have made an important contribution to the poultry industry.
The percentage of mortality from Angara disease in unvaccinated half-meat herds and immature maternal herds if accompanied by Newcastle disease and Gam borough disease is more than 80%.The infection is usually between 9 and 14 days, the percentage of infection is 10 to 30 percent, and there are 3 to 5 percent daily fatalities.
The herds involved in Angara Don’t have specific clinical symptoms. The sudden onset of fatalities, lethargy, gathering in one spot, tangled yellow feathers and shedding are full of characteristic symptoms.
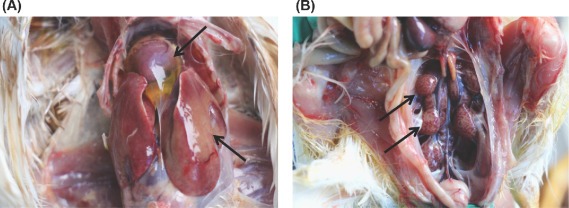
There are general bloodstained carcasses and lung edema. The liver and kidneys are large and pale and crisp and fragile. In vitro in poultry, myocardial necrosis and liver necrosis is observed. Bleeding may be seen on the pericardium and liver capsule.
Fowl adenovirus serotype 4(FAdV-4) For chickens, especially chickens aged 3 to 5 years are very pathogenic, and this disease is also seen in immature poultry and commercial laying hens In the areas where the disease occurs, it may be associated with other poultry diseases such as Newcastle and Marek and the Influenzas.
The main organ targeted for FAdV-4 infections, liver, and broilers infected with the virus usually show signs of hydropericardium syndrome, the virus is highly contagious.
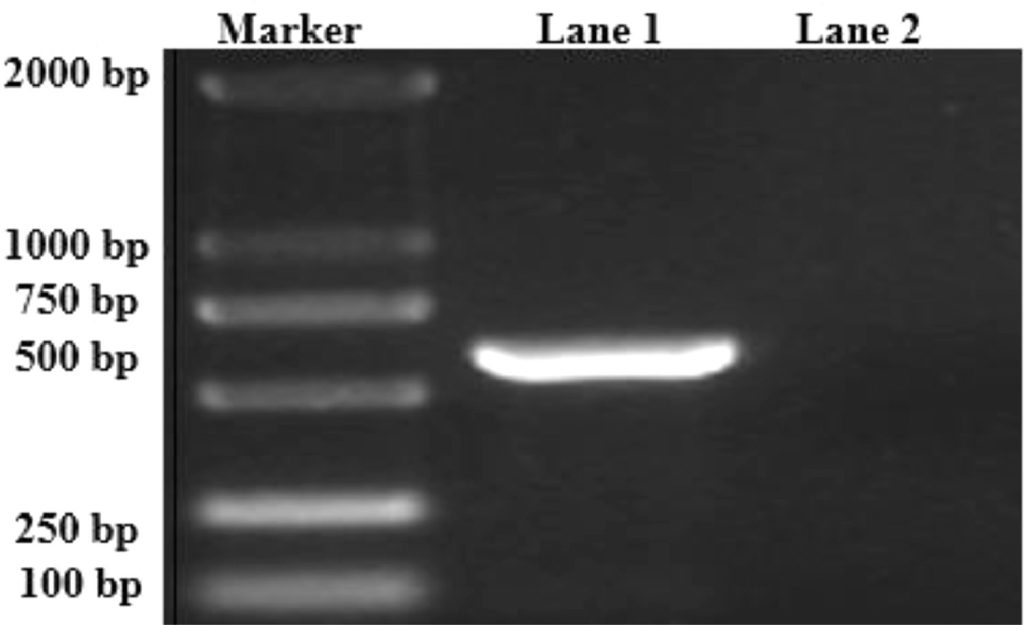
Identification of FAdV-4 by RT-PCR
In this identification by sampling fowl liver tissue, fowl liver DNA is extracted and used as a model for PCR assay. The results showed that the DNA replicated from the liver of the patient fowl in a specific band of 599bp was obtained.
To prevent Angora disease، recommendations should be followed:
- Considering minimum distance of 2 km between the farm and agricultural and commercial units as well as the implementation of cleaning and disinfection of halls in consecutive breeding periods
- The feed must be carried into the poultry farm by special machines for carrying the indoor feed and all persons and employees must observe hygiene and disinfection issues before entering the farm.
- Wild birds such as pigeons and crows should be prevented from entering the barn and poultry breeding halls.
- Vaccinations should be done to prevent infection.

Write Your Comment