A biological hazard is created by a biological substance that poses a threat to living organisms, primarily involving humans. This can include an example of a microorganism, virus or toxin that can adversely affect human health. A biohazard can also be a substance that is harmful to other living organisms.
The main biological hazards in food include bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi, all of which can have severe health effects on humans and animals. Changes with previous microorganisms can occur during crop growth, harvesting, storage, transportation, post-processing or distribution and lead to serious product and economic problems. Microorganisms are usually identified by genomic analysis (polymerase chain reaction, PCR) culture or immunoassay. In any case, microbial detection is in the early stages for the food industry and consumer consumption, and biosensors can be very fast providers of useful analytical results for this purpose.

Smart protection against chemical and biological hazards is neutralizing the effect of the threat. The purpose of these self-depleting membranes is twofold. First, it limits secondary contamination and avoids putting unprotected people at risk, secondly, it aims to prevent the progress of pollutants because they gradually progress with the pollutants that are present.
Also, in farms, the initial investigation of biological risks should be done at the level of entry or exit of each animal from the farm, as well as monitoring the re-entry of a healthy animal. A newly introduced animal should be thoroughly checked for infection and vaccination status. It should be tested on common animal diseases in that area, and after identifying the infected animal, it should be kept separately for the quarantine period. Entry of personnel should be limited and no new person from unknown area or native area should be allowed to enter the farm. The entry of vehicles should also be cautious and limited.
Campylobacter and Salmonella are the main pathogens associated with foodborne illness, and a variety of foodborne biohazards are associated with chicken and eggs. It is estimated that 44 to 68 percent of human foodborne Salmonella cases are related to contamination from human hands, egg preparation, and consumption, while only 4 to 7 percent are related to meat, beef, and turkey. In contrast, 20–30% of human foodborne Campylobacter cases are related to contamination from human hands, preparation, and consumption of broiler and turkey meat (or 60–80%, considering cross-contamination pathways in the kitchen). be).
Invasive alien species are defined as species present in an area as a result of human actions with harmful effects on communities and the environment, such as reducing crop yields, damaging critical infrastructure, and disrupting the provision of ecosystem services.
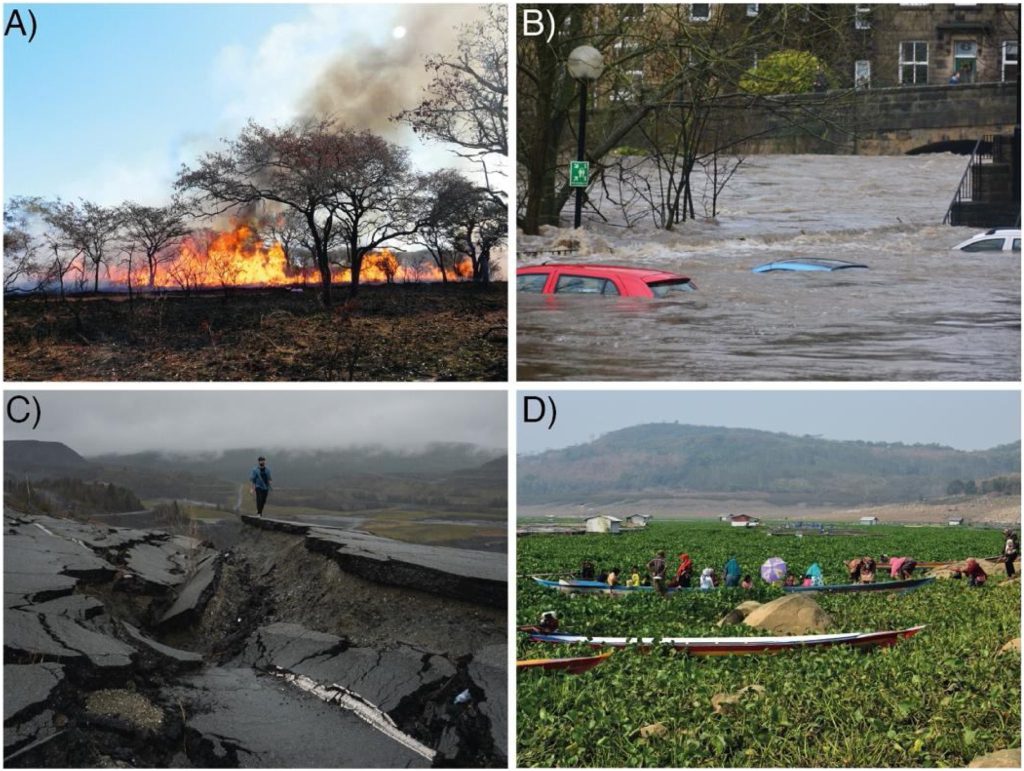

In the picture above, you can see natural hazards and alien species.
This lack of awareness and concern is more noticeable when fire hazards such as earthquakes, floods and fires have created attention and investment for social attention to reduce or adapt. In fact, biological invasion and natural hazards are comparable with remarkable similarities such as dynamics and difficulties in prediction and control.
What are the four types of biological hazards?
Biological factors
Some examples of biological hazards under this classification include bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi (such as yeasts and molds). These are usually considered harmless if controlled, while some of them may cause serious risks and diseases to animals or humans such as the COVID-19 virus.
Biotoxins
These refer to a group of substances of biological origin that are toxic to humans. Often, biotoxins are produced by certain plants, bacteria, insects, or animals. Continued exposure to these may cause at least a series of inflammatory reactions throughout the body.
Blood and blood products
While blood is not considered a biohazard, it can pose potential risks if it is contaminated or the source is contaminated in any way. Also, blood products such as red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, tissues and platelets are also dangerous if not handled properly. Environmental samples Generally, this refers to plants, soil or water that potentially contain the first two types of biological hazards – biological agents and biotoxins.
In light of the Corona virus pandemic that engulfed the whole world, it was a wake-up call that warned countries to prepare for the “worse”.
For this purpose, Milad Daru Company has produced biological, chemical and nuclear products for protection in these special conditions and also with the existing infrastructure in the vaccine factory, it has declared its readiness to face these conditions.
Write Your Comment